Stanford researchers reveal how AI tools — from chatbots to predictive models — could revolutionize public health research by giving communities a stronger voice, while also grappling with AI’s ethical dilemmas.
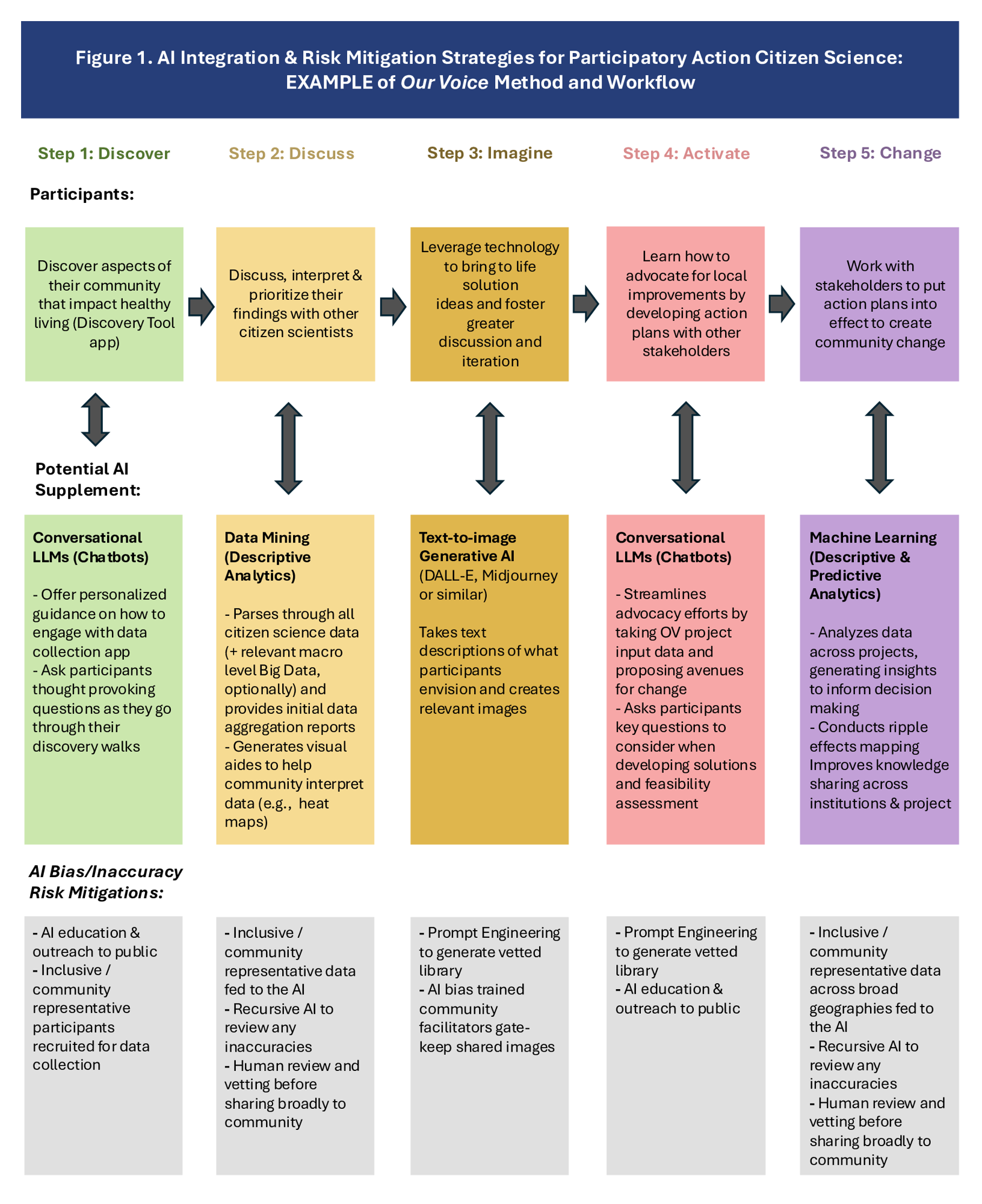 Artificial intelligence (AI) integration and risk mitigation strategies for participatory action citizen science: example of “Our Voice” Method and workflow. LLM: large language model; OV: Our Voice.
Artificial intelligence (AI) integration and risk mitigation strategies for participatory action citizen science: example of “Our Voice” Method and workflow. LLM: large language model; OV: Our Voice.
A new study published in JMIR Public Health and Surveillance by a team from Stanford Medicine investigates the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) to revolutionize citizen science and advance health equity. The study "The Promise and Perils of Artificial Intelligence in Advancing Participatory Science and Health Equity in Public Health" explores how AI technologies can empower communities to participate actively in scientific research and address critical ethical considerations.
This research, published by JMIR Publications, examines the potential of AI to significantly enhance citizen science by enabling more inclusive and impactful projects. It ultimately aims to advance health equity and public health outcomes.
Several promising AI applications are discussed in the study, including:
-
Conversational AI: Large language models can facilitate more accessible and engaging interactions between researchers and citizen scientists, breaking down communication barriers and enabling more inclusive participation.
-
Generative AI: Tools like text-to-image AI can assist in data visualization, making research findings more understandable and engaging for the public.
-
Predictive analytics: AI can analyze large datasets to identify trends and predict potential public health risks, empowering communities to address emerging challenges proactively.
The study also acknowledges the potential risks associated with using AI in citizen science, such as bias in AI algorithms, data privacy concerns, and the potential for AI to exacerbate existing inequalities. The researchers emphasize the importance of responsible AI development and implementation, including robust ethical frameworks and ongoing community engagement.
One of the authors has provided a video discussion of the paper's key points to help explain the research.
Unveiling Dementia Advocacy Strategies on Social Media
Source:
Journal reference:
- King AC, Doueiri ZN, Kaulberg A, Goldman Rosas L The Promise and Perils of Artificial Intelligence in Advancing Participatory Science and Health Equity in Public Health JMIR Public Health Surveill 2025;11:e65699 doi: 10.2196/65699, https://publichealth.jmir.org/2025/1/e65699