The advancement of AI has faced challenges in understanding and navigating complex 3D environments. Traditional methods often depend on extensive datasets and predefined models, restricting an agent's adaptability in dynamic settings. Recent developments aimed to overcome these limitations through advanced algorithms capable of generating realistic, coherent environments from minimal input.
Generative AI leveraged deep learning techniques like neural networks to synthesize new data from existing patterns. Widely applied in image generation, natural language processing, and simulations, this technology uses scalable 3D data from platforms like Unreal Engine to create immersive environments with realistic physics and visual coherence.
This technology integrates two core components: a generative model that constructs dynamic 3D spaces and an embodied agent that interacts with these environments. The generative model creates adaptive virtual worlds, while the agent refines its understanding and decision-making through exploration. Together, they enable AI to perform human-like cognitive tasks, including reasoning and problem-solving, in interactive and realistic settings.
GenEx: A Novel System for Creating a Virtual Explorable World
In this paper, the authors presented GenEx, an innovative system to generate explorable worlds that are both visually coherent and physically plausible. Using a single RGB image as a starting point, their system aimed to generate a full 360-degree panoramic representation, enabling AI agents to engage in realistic explorations.
GenEx: Generating an Explorable World
The methodology involved training a generative model on data sourced from physics engines, ensuring that the generated environments align with real-world physics. The process begins with world initialization, where an initial panoramic view is generated based on the input image and a corresponding textual description. This is followed by world transitions, allowing the agent to navigate through the environment by sampling new views based on actions like movement and rotation.
By reformulating the exploration task as a video generation problem, the researchers introduced a novel framework that enables AI agents to refine their beliefs and simulate various outcomes based on their decisions. The system's performance was evaluated using metrics such as Fréchet Video Distance (FVD) and Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM), which demonstrated GenEx's high-quality generation capabilities. The system maintains loop consistency over extended trajectories, ensuring the generated environments remain coherent and relevant throughout the agent's exploration.
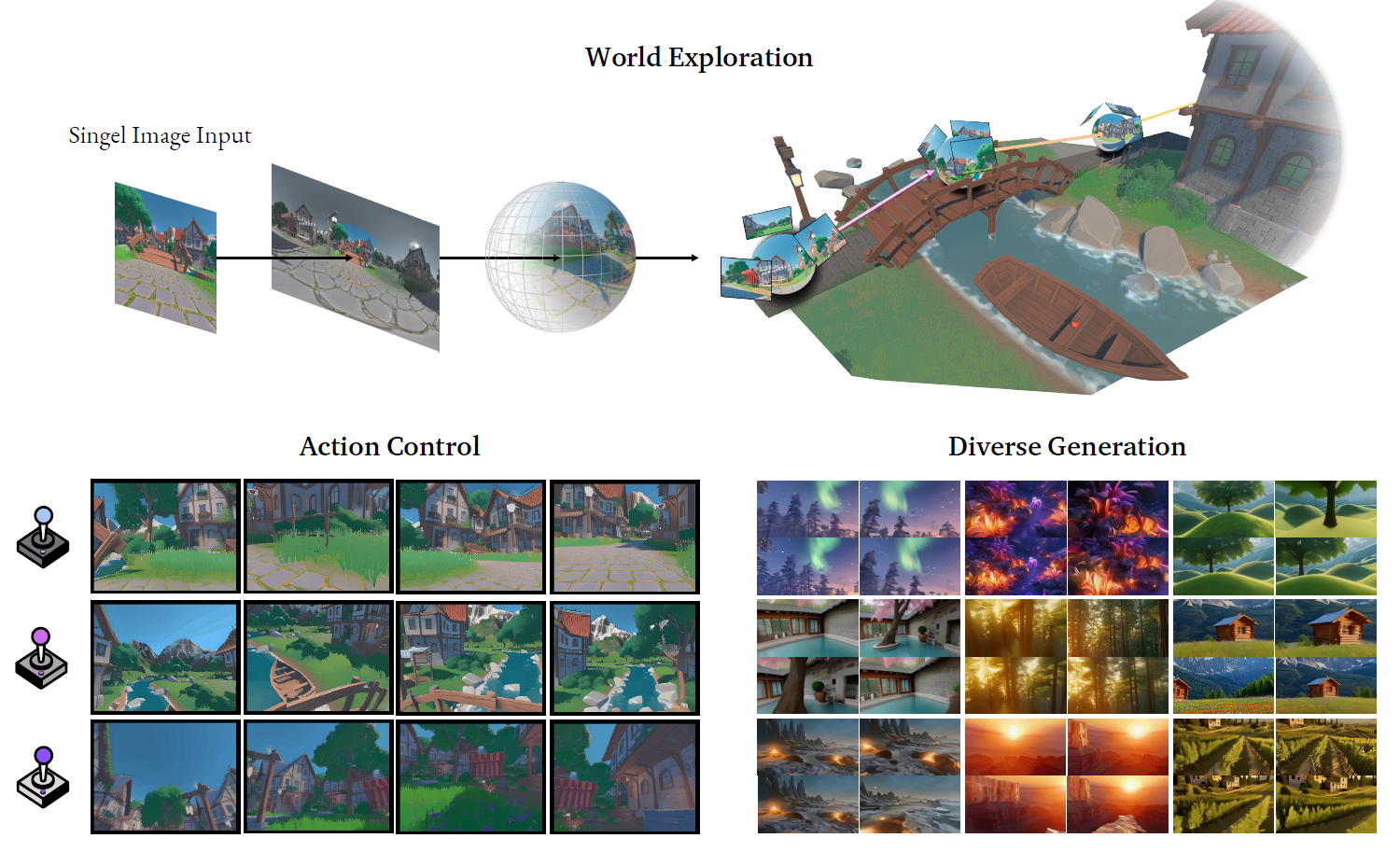 GenEx explores an imaginative world, created from a single RGB image and brought to life as a generated video. See more examples in our website (genex.world).
GenEx explores an imaginative world, created from a single RGB image and brought to life as a generated video. See more examples in our website (genex.world).
Key Outcomes
The study highlighted key aspects of the system's performance and its implications for AI. A notable finding was the system’s ability to generate high-quality, immersive environments with robust 3D capabilities. These environments not only captured intricate visual details but also adhered to physical principles, enabling realistic interactions for AI agents.
The authors emphasized the importance of generative imagination in enhancing exploratory behavior. By forming predictive expectations about unseen areas, agents were able to make informed decisions and simulate potential outcomes. This functionality proved especially effective in multi-agent scenarios, where agents could share imagined beliefs and optimize their exploration strategies collaboratively.
The introduction of the Imaginative Exploration Loop Consistency (IELC) metric further validated the system's robustness. Results showed minimal visual drift, with latent mean squared error (MSE) below 0.1, even for extended exploration loops.
Practical Applications
This research has significant implications across various domains, including real-world navigation, interactive gaming, and virtual reality (VR) environments. The ability to generate explorable worlds from minimal input can enhance user experiences in gaming and training simulations, where immersive environments are vital for engagement and effective learning.
Additionally, the framework has applications in robotics, enabling robots to navigate complex environments autonomously. The potential for real-time exploration and decision-making paves the way for advancements in autonomous systems, allowing them to adapt to dynamic situations and make informed decisions based on their surroundings.
However, challenges remain, including the need for sim-to-real adaptation, integration with real-world sensors, and addressing dynamic conditions in unpredictable environments. Future work must also address ethical considerations to ensure safe deployment in diverse settings.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In summary, this study demonstrated the transformative potential of generative AI in advancing embodied AI. By combining generative imagination with physical world modeling, GenEx proved to be a new approach for exploring and understanding complex environments. The findings underscore the importance of creating coherent and immersive worlds while also paving the way for future research in AI-driven exploration.
As the field evolves, the implications of this work suggest that further advancements in generative AI could lead to more advanced applications across various sectors, including education, entertainment, and autonomous navigation. The researchers highlighted ongoing efforts by organizations like WorldLabs and DeepMind in similar areas, situating GenEx within a broader context of advancing AI-driven world generation. The continued development of these systems will play a crucial role in shaping the future of AI, enabling agents to explore, learn, and interact in ways that closely mirror human cognitive processes.
Introducing GenEx

 *Important notice: arXiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as definitive, used to guide development decisions, or treated as established information in the field of artificial intelligence research.
*Important notice: arXiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as definitive, used to guide development decisions, or treated as established information in the field of artificial intelligence research.
Source:
Journal reference:
- Preliminary scientific report.
Lu, T., & et al. GenEx: Generating an Explorable World. arXiv, 2024, 2412, 09624. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2412.09624, https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.09624